1.) Add a non root user:
If you connect to your server via ssh you should never connect using the root user.
Example:
ssh root@<ip-address>
Add a non-root user:
adduser <username>
Output:
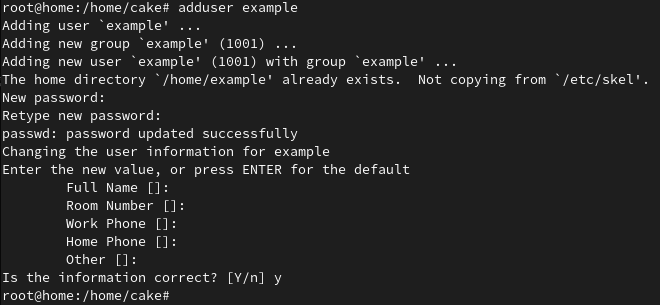
Enable sudo for the user:
usermod -a -G sudo <username>
-a: add (append)
-G: Groups
-a -G means add user to Group …
Switch to the new user:
su <username>
2.) Change the default ssh port:
By default the ssh protocol uses the port 22. This should be changed to make it harder for a Hacker to attack the server.
Change the default ssh port:
Edit the default port in the sshd_config file.
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Look for a line like this.
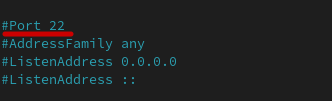 Remove the # and change the number from 22 to any number from 1025 - 49000
Remove the # and change the number from 22 to any number from 1025 - 49000
Example:
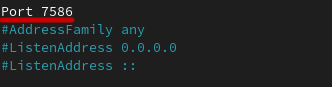
Now restart the ssh service:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
3.) Login using a ssh-keypair
By usoing ssh-keys you are much more secure and do not even have to type a password using public and private keys.
Create the ssh-keypair:
On your PC (NOT the server) open the Powershell or the Terminal and generate a ssh-keypair
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
-t: type
-b: bits
This command will generate a rsa key with 4096 bits
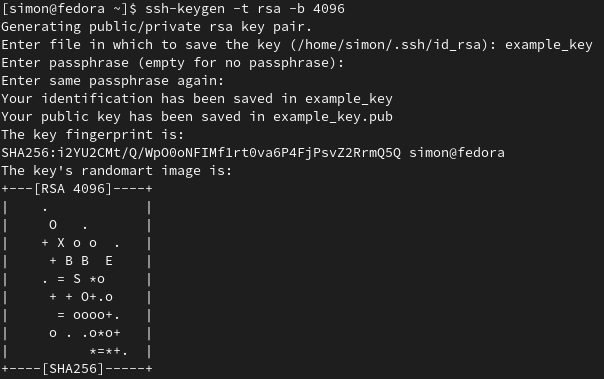 If you hit ENTER all the time the file
If you hit ENTER all the time the file id_rsa is now in the .ssh/ directory if you gave th file a name it should be in the current directory.
Copy the public key to your server:
If you hit always ENTER:
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
or
If you gave it a custom filename:
cat <filename>.pub
Example:
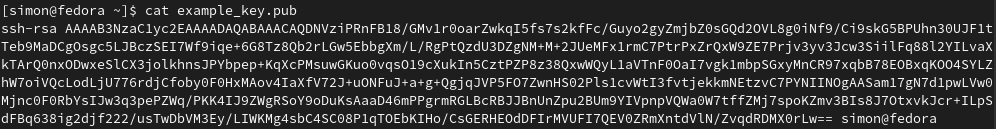
Now copy everything and paste it into the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file on your SERVER.
mkdir ~/.ssh/
and
nano ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Inside the nano text editor paste the content of the public key wich was read using the cat command. You can save the file by pressing STRG+O and ENTER
Disable loggin with password:
Since we can now login with our just created ssh-keypair we can disable login with password over ssh. Again edit the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Look for PasswordAuthentication yes and change it to PasswordAuthentication no
Example:
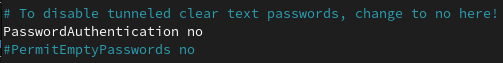
The only thing left to-do is to restart the ssh service.
sudo systemctl restart ssh
Now you are done you can acces your server by typing:
ssh <username>@<ipaddress> -p <port>